06 - Analysis of StealC (Stage 4)
In the first article of the series, we saw how to unpack the first stage pkr_ce1a manually and using an emulator (MIASM). In the second article we have extracted the C2 of the loader and unpacked the last stage using MIASM. Now let's take a look at the StealC malware and recover some IOCs.
Sample information
Below is the information concerning the last stage we are going to analyze:
| Type | Data |
|---|---|
| SHA256 | 18f53dd06e6d9d5dfe1b60c4834a185a1cf73ba449c349b6b43c753753256f62 |
| SHA1 | a952b1ed963346d5029a9acb3987d5e3a65c47a3 |
| MD5 | 8022ef84cfe9deb72b1c66cd17cac1cd |
| File size | 153 088 bytes |
| First seen | N/A |
| MIME type | application/x-dosexec |
| imphash | 1ef0d6e4c3554a91026b47d9a27bf6db |
| ssdeep | 3072:ivyLlG8KPgpJSG61doHN4NoQiUukOoy9bzyRy2GxhGJuU:ivyhJryZoIohvkOpt+M2GzAu |
At the time of writing, the sample has not been made public on sample-sharing platforms such as VirusTotal.
Detect the sample family
First, we can look at the entropy of the file to see if it is packaged:

The latter is not packaged, as its entropy is not high.
We don't know which family of malware it is yet. A loader? A beacon? To find out, we can run a Yara scan. If you don't have a Yara rules database, you can find some on GitHub repositories such as Yara-Rules (no longer maintained), or on specialized platforms such as Malpedia.
If you run a scan on all Malpedia's Yara rules, you should come across a positively matching rule named win_stealc_auto:
$ yara -s win.stealc_auto.yar syncUpd_exe_miasm_unpacked.bin
win_stealc_auto syncUpd_exe_miasm_unpacked.bin
0x135df:$sequence_0: FF 15 38 4F 62 00 85 C0 75 07 C6 85 E0 FE FF FF 43
0xde4c:$sequence_1: 68 6F D7 41 00 E8 EA 82 00 00 E8 65 E7 FF FF 83 C4 74
0xc760:$sequence_2: 50 E8 3A 9A 00 00 E8 D5 F2 FF FF 83 C4 74
0xc81c:$sequence_2: 50 E8 DE 40 FF FF E8 D9 EC FF FF 83 C4 74
0xc8ca:$sequence_2: 50 E8 70 98 00 00 E8 EB FC FF FF 83 C4 74
0xaf51:$sequence_3: E8 4A B2 00 00 E8 D5 E4 FF FF 81 C4 80 00 00 00 E9 53 03 00 00
0xb03c:$sequence_3: E8 5F B1 00 00 E8 EA E3 FF FF 81 C4 80 00 00 00 E9 68 02 00 00
0xd558:$sequence_4: 50 E8 42 8C 00 00 E8 DD F3 FF FF 81 C4 84 00 00 00
0xd5d4:$sequence_4: 50 E8 C6 8B 00 00 E8 61 F3 FF FF 81 C4 84 00 00 00
0xd650:$sequence_4: 50 E8 4A 8B 00 00 E8 E5 F2 FF FF 81 C4 84 00 00 00
0x124c7:$sequence_5: E8 44 25 FF FF 83 C4 60 E8 7C E2 FF FF 83 C4 0C
0x10692:$sequence_6: E8 09 5B 00 00 E8 A4 4A FF FF 83 C4 18 6A 3C
0x149d6:$sequence_7: FF 15 88 50 62 00 50 FF 15 20 50 62 00 8B 55 08 89 02
0x149dc:$sequence_8: 50 FF 15 20 50 62 00 8B 55 08 89 02
It seems that the executable matches 9 out of 10 sequences, which is a very good score. We can therefore strongly assume that this is the final StealC malware. Malpedia has a dedicated page about it.
Our aim is to recover C2 from the malicious program, and several methods can be used:
- Sandbox
- Emulation
- Static analysis
In this article, we will use the Static method.
Automate string decryption
Open the sample with your favorite disassembler. By wandering through the various functions, you should be able to identify methods calling sub_4043b0 which seems to take 3 parameters: a sequence of bytes, a string, then an integer (which seems to correspond to the length of the string):

If we unpack the sub_4043b0 function, we can see that the malware uses a military encryption algorithm (xor). We can rename the function and its variables:
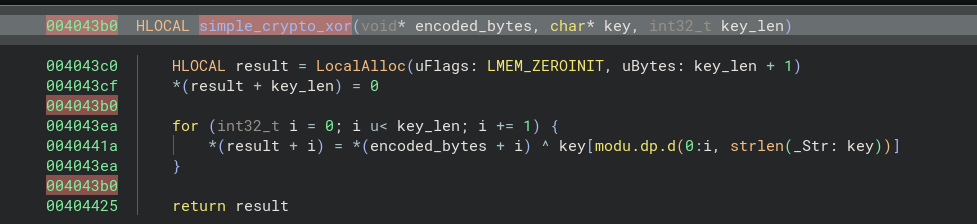
The function we just renamed simple_crypto_xor is used by two other functions in the program:
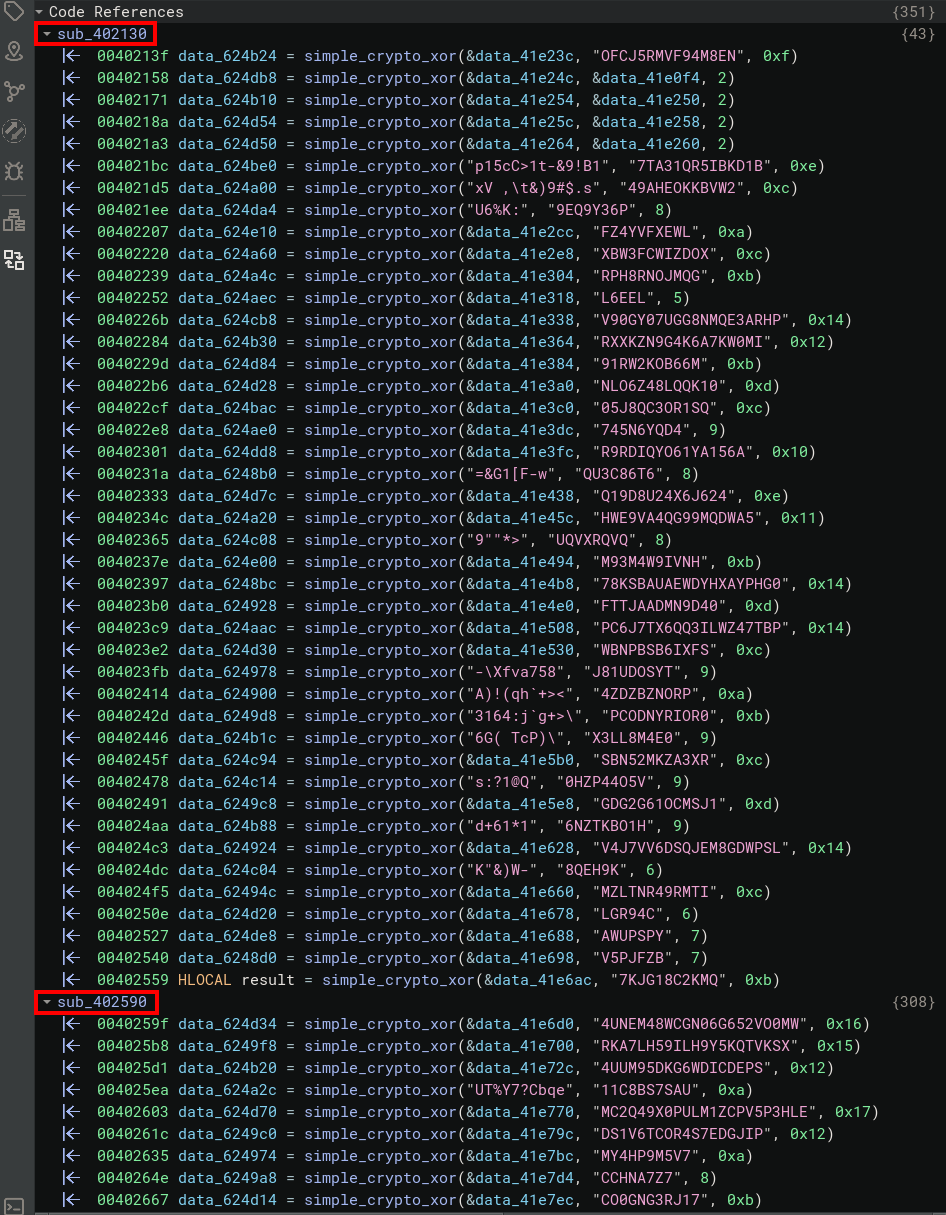
We can then rename the variables according to the bytes decoded with our disassembler's API. First, we'll try to recover the address of the function that performs the XOR operations, based on the calls to the LocalAlloc and strlen functions:
def get_most_called_function_sorted():
funcs = bv.functions
call_function_counter = {}
for func in funcs:
callers = func.callers
#print("\nFunction {} is called from {} known locations.".format(func.name, len(callers)))
call_function_counter[func] = len(callers)
return sorted(((v, k) for k, v in call_function_counter.items()), reverse=True)
def get_xor_str_func():
most_called_functions = get_most_called_function_sorted()
for func in most_called_functions:
if func[0] < 260:
# xor func must have more than 100 callers
break
if not func_has_call_func_by_name(func[1], "LocalAlloc"):
continue
if not func_has_call_func_by_name(func[1], "strlen"):
continue
return func[1]
return None
def func_has_call_func_by_name(func, func_name: str):
for inst in func.mlil.instructions:
if not isinstance(inst, Localcall):
continue
if str(inst.dest) == func_name:
return True
return False
Once we have the address of our simple_crypto_xor function, we can try to identify the functions that call it, retrieve the arguments sent as parameters and then decode them. Once decoded, we can then rename the destination variables to make them easier to read:
[...]
xored_str = None
def xorme(secret_string, key, key_len):
final = ""
for i in range(0, key_len):
final = f"{final}{chr(secret_string[i] ^ key[i])}"
return final
def visitor_xored_func(_a, inst, _c, _d) -> bool:
global xored_str
if isinstance(inst, Localcall):
ptr_secret_string = int(inst.params[0].value)
key = inst.params[1].string[0].encode()
key_len = int(inst.params[2].value)
secret_string = bv.read(ptr_secret_string, key_len)
xored_str = xorme(secret_string, key, key_len)
def main():
global xored_str
xor_func = get_xor_str_func()
if not xor_func:
print("Error: StealC xor func not found")
return
print(f"Xor function at @{xor_func.address_ranges}")
xor_func_callers = []
callers = xor_func.callers
for caller in callers:
if caller in xor_func_callers:
continue
xor_func_callers.append(caller)
for inst in caller.hlil.instructions:
xored_str = None
inst.visit(visitor_xored_func)
if xored_str:
try:
dst = inst.dest.get_expr(0).get_int(0)
var = bv.get_data_var_at(dst)
print(f"New string identified : {xored_str}")
xored_str_cleaned = xored_str.replace("/", "-").replace("%", "").replace(":", "").replace(" ", "_").replace(".", "_").replace("/", "_").replace("\\", "_").replace(",","_")
var.name = f"str_{xored_str_cleaned}" # Rename variable
except:
pass
main()
This produces the following result:
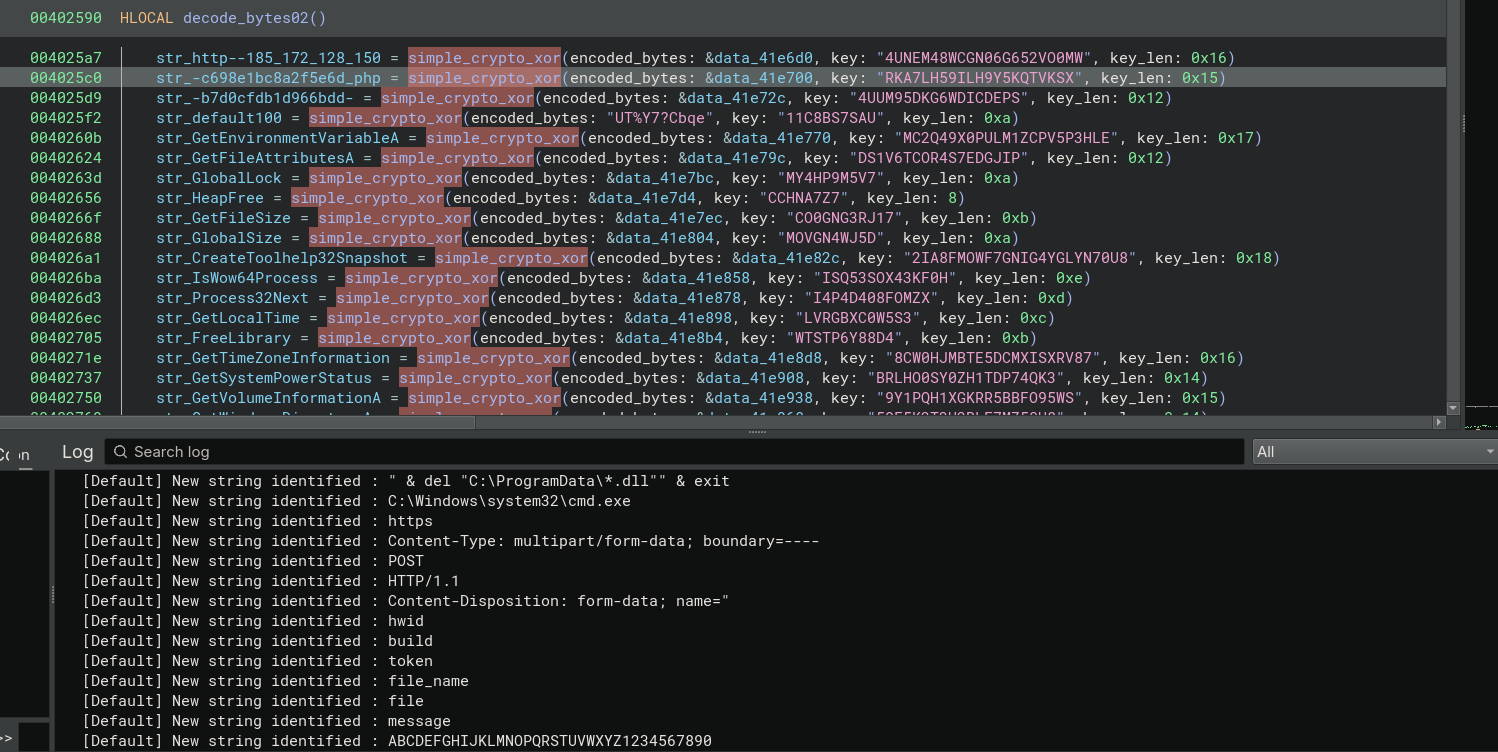
Lists of decoded strings are available here.
Looking at the decoded strings, we learn a lot more about our malware! Some notable features:
- It seems to use the HTTP protocol to communicate
- An IP address is decoded:
185[.]172.128.150 - A web page:
c698e1bc8a2f5e6d.php - A directory on the web server:
/b7d0cfdb1d966bdd/ - Possibly anti-vm:
VMwareVMware - Possible recovery of identifiers in web browsers
- Possible login recovery in software such as Discord, Steam Pidgin, Outlook, Telegram, Tox...
- Recovery of elements of the system configuration of the machine running the program
- Potential recovery of cryptocurrency wallets
From the strings alone, we can deduce that specific method will be loaded into memory and then called. We won't be performing a Stealer (StealC) analysis.
Static sample analysis
You can continue the analysis by tracing function calls back to the decoded strings. For example, our str_CreateToolhelp32Snapshot variable appears to be loaded into memory:
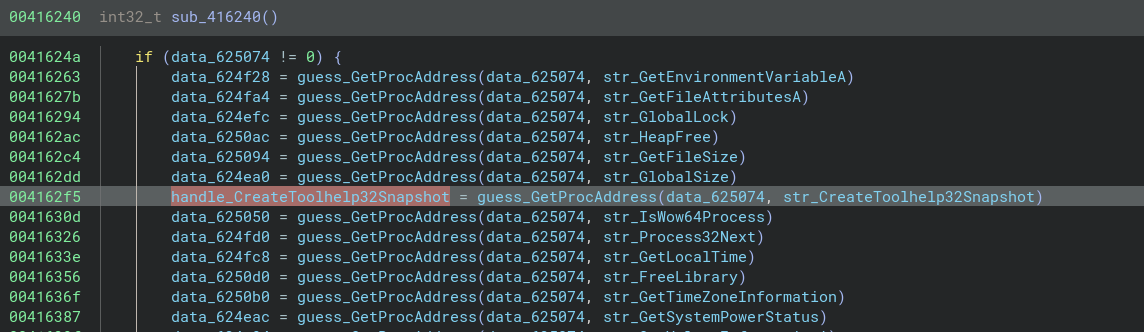
We rename the variable to handle_CreateToolhelp32Snapshot, we look for cross references to this handle and we can see its call later in the program:
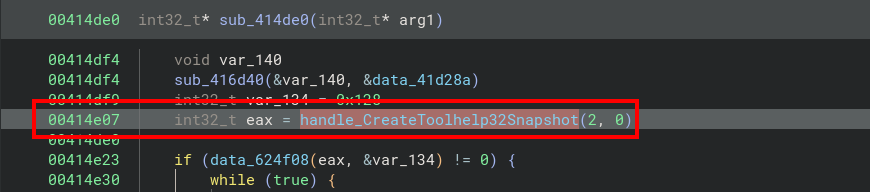
Now that you've got all the marbles, you should be able to automate the renaming of the various functions loaded in memory, and study the part of the malware you're interested in. Our bndb file is available here.
You'll find here the code used to retrieve the complete C2 used by the StealC malware we've just studied.
07 - Conclusion
In this series of articles (part1, part2, part3), we have outlined various techniques for analyzing a malware sample active in 2024. We hope that this article has permit you to understand some of the methods used to:
- identify some packers
- unpack in manual and automated ways
- write detection rules (Yara)
- extract the interesting parts, such as C2, to help you protect your company and those around you.
You have handled a disassembler and a debugger for Stage 1 unpacking. You also got an overview of the MIASM framework and the possibilities offered by its jitter sandbox. You have seen some methods used by malicious actors to make analysis more difficult, using anti-emulation techniques. We've also seen how to automate most of our actions, such as extracting and decrypting shellcode from program resources. You've also had a taste of how to automate tedious tasks such as renaming encrypted variables in your favorite disassembler.
You should be able to set out on your own in search of new samples to analyze, and have the perseverance to overcome the technical problems you'll encounter, given a few liters of coffee and time.
Thanks to zbetcheckin for sharing the initial sample with the community. Thanks also to the MIASM contributors who produced a very practical and functional tool in our case. Thanks to the Binary Ninja developers and community for the various exchanges we were able to have. Thanks to the malware researchers who share their research on threats targeting cyberspace.
We hope this series of articles has motivated you to continue analyzing malicious code! Please don't hesitate to contact us if you'd like us to clarify any aspect of the articles, or if you have any questions we'd be happy to answer. We can also support you in malware analysis, or train you in this area.
We will shortly be publishing an article dedicated to the packer pkr_ce1a aka AceCryptor which protects malicious binaries like StealC seen in these articles. Stay tuned !
